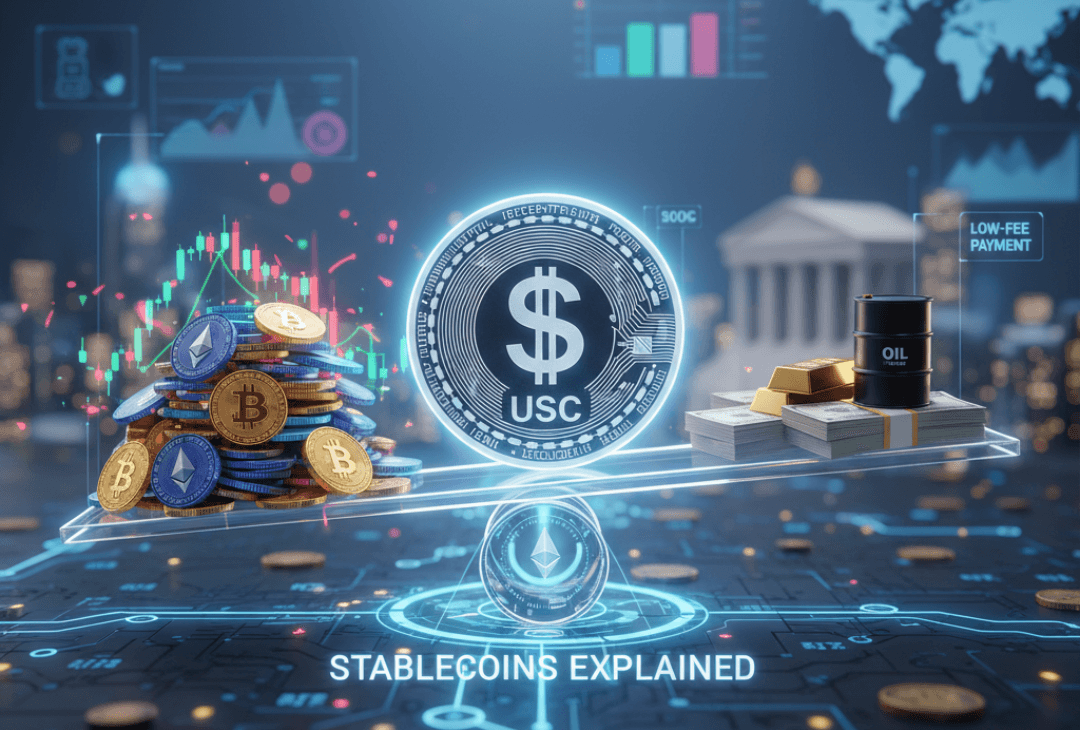
In the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrencies, one concept stands out for its balance between innovation and stability — stablecoins. These digital assets are designed to maintain a consistent value by being pegged to other assets like fiat currency, commodities, or even cryptocurrencies. Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum, whose prices can swing wildly, these assets aim to offer reliability in an unpredictable market.
The Mechanism: How Stablecoins Achieve Stability
There are several reasons why investors and everyday users are turning to stable assets:
- Price Stability: Volatility is the biggest challenge in crypto trading. Stable assets offer a way to hold value without worrying about price fluctuations.
- Ease of Transactions: They are widely used for sending money globally with low fees and near-instant speed — no intermediaries needed.
- Hedging Against Volatility: Traders often park profits in these tokens between trades to protect their gains from market downturns.
- Access to DeFi: Stable assets serve as the backbone of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), allowing users to lend, borrow, and earn interest.
- On-Ramp for Crypto Beginners: Since the value is predictable, newcomers find it easier to start with these assets rather than volatile tokens.
Diverse Applications in Digital Finance
These tokens have found diverse applications across the digital finance ecosystem:
- Trading Pairs on Exchanges: Most crypto exchanges offer trading pairs in USDT or USDC instead of fiat money.
- Cross-Border Remittances: Sending money using these digital tokens is cheaper and faster compared to traditional wire transfers.
- Smart Contracts: Users implement them as payment tokens in automated blockchain agreements.
- Yield Farming and Lending: In DeFi platforms, users earn interest by lending or staking their stable digital assets.
- E-commerce Payments: Some merchants now accept these tokens due to their predictable value.
The Mechanism: How Stability is Achieved
The underlying mechanism revolves around maintaining a peg to another asset, typically priced at a ratio of 1:1. Different assets achieve this stability through varying models:
- Asset Collateralization: The issuer holds reserves equivalent to the coin’s value.
- Smart Contract Algorithms: An automated system adjusts supply and demand to stabilize the price.
- Trust and Audits: Some issuers maintain transparency through regular reserve certifications, which an outside firm often conducts.
Diverse Backing Models
Not all stable assets are backed solely by cash. While fiat-backed coins like USDT (Tether) and USDC (USD Coin) hold reserves in dollars or short-term treasuries, others rely on algorithmic systems or crypto collateral. Each model carries its own level of risk and transparency.
The Main Categories of Stable Digital Assets
We can classify these assets into several main types based on their collateral:
1. Fiat-Backed Tokens
- Mechanism: Backed by fiat currency reserves like USD or EUR stored with banks or custodians.
- Example: USDC, Tether (USDT).
- Note: They are the most popular and least volatile category due to the trust placed in real money reserves.
2. Crypto-Backed Tokens
- Mechanism: Instead of fiat, other cryptocurrencies back them. Due to volatility, the collateral is often overcollateralized (holding more crypto value than the token value) to ensure ongoing stability.
- Example: DAI [https://makerdao.com], which uses Ethereum-based collateral.
3. Commodity-Backed Tokens
- Mechanism: These are tied to commodities like gold or oil.
- Example: PAX Gold (PAXG), where each token represents ownership of physical gold. Investors use them to diversify their portfolios while retaining stability.
4. Algorithmic Tokens
- Mechanism: Rather than relying on reserves, smart contracts automatically regulate the supply. When demand increases, the contracts issue new tokens; when it falls, the supply is reduced (burned).
- Example: Ampleforth and Frax.
- Note: This model can be fragile during extreme market conditions.
Key Drawbacks and Risks
Despite their advantages, these digital assets are not risk-free:
- Lack of Transparency: Some issuers fail to provide clear details about reserve holdings.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments are still defining how they will classify and control these assets.
- Centralization Risks: Centralized entities control the reserves and issuance of fiat-backed coins.
- Algorithmic Collapse: History shows that an algorithmic asset can lose its peg rapidly in market downturns (e.g., the TerraUSD crash).
- Liquidity and Redemption Issues: In times of crisis, users may find redeeming their tokens for fiat difficult.
Are Stablecoins the Future of Money?
Stablecoins bridge traditional finance and blockchain technology, making global payments faster and cheaper. Central banks have even begun exploring Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) based on similar principles.
While these tokens are not perfect, their ability to provide price stability within the crypto ecosystem sets them apart as a powerful financial innovation.
In the future, we may see governments and private firms collaborating on hybrid models — combining the security of fiat reserves with blockchain efficiency. As adoption grows, these assets could evolve from trading tools into everyday mediums of exchange.
Final Thoughts
Stablecoins are reshaping how we perceive money — merging digital speed with financial stability. Whether you are an investor, trader, or curious learner, understanding this asset class is essential to navigating the modern crypto landscape. As regulation matures and technology improves, stablecoins might just become the bridge to a fully decentralized world economy.
Last modified: October 16, 2025




Nicely done